| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- SCC
- Prisma
- LCA
- 그래프 탐색
- map
- 강한 연결 요소
- 이분 탐색
- Github
- Spin Lock
- Binary Lifting
- 벨만-포드
- Lock-free Stack
- Behavior Design Pattern
- 자바스크립트
- Strongly Connected Component
- PROJECT
- 2-SAT
- JavaScript
- 게임 서버 아키텍처
- 비트마스킹
- 비트필드를 이용한 dp
- R 그래프
- ccw 알고리즘
- 분리 집합
- DP
- trie
- 최소 공통 조상
- 트라이
- localstorage
- Express.js
Archives
- Today
- Total
dh_0e
[C++/Game Server] DeadLock Profiler (+ release, debug 모드) 본문
DeadLock Profiler (데드락 탐지)
- DeadLock을 탐지하는 Profiler를 구성하여 RW Lock과 함께 사용
- Lock으로 visit check, dfs로 그래프 탐색하면서 사이클(DeadLock)을 찾는 방식
DeadLockProfiler.h
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
/*--------------------
DeadLockProfiler
---------------------*/
// lock으로 visit check 하면서 그래프 탐색하는 느낌
class DeadLockProfiler
{
public:
void PushLock(const char* name);
void PopLock(const char* name);
void CheckCycle();
private:
void Dfs(int32 index);
private:
unordered_map<const char*, int32> _nameToId;
unordered_map<int32, const char*> _idToName;
stack<int32> _lockStack;
map<int32, set<int32>> _lockHistory;
Mutex _lock;
private:
vector<int32> _discoveredOrder;
int32 _discoveredCount = 0;
vector<bool> _finished;
vector<int32> _parent;
};- Lock 지도(상태) 데이터
- _nameToId: "AccountLock" 같은 name을 고유한 숫자 id로 바꿔서 관리하기 위한 표
- _idToName: 데드락 발생 시 "1번 lock"이 아니라 "AccountLock"이라고 이름을 찍어주기 위한 역참조 표
- _lockStack: (스레드별) 현재 내가 어떤 락을 잡고 그 위에 또 뭘 잡았는지 순차적으로 기록하는 장부
- ※ 사실 DeadLockProfiler가 아니라 각 스레드별로 TLS에 저장해야 하는 부분임 (추후 수정 예정)
- _lockHistory: "A 락 다음엔 B 락을 잡더라"는 전역적인 모든 락 연결 관계(간선)를 모아놓은 전체 지도
- CheckCycle(DFS)에 사용될 데이터
- _discoveredOrder: 노드가 발견된 순서를 기록하는 배열 / DFS 탐색 중 몇 번째로 방문한 노드인지 기록해 "나보다 먼저 방문한 조상"을 찾을 때 사용
- _discoveredCount: 현재 발견된 노드의 개수로, 방문 순서를 0, 1, 2... 순으로 하나씩 번호를 매겨주기 위한 카운터
- _finished: 해당 노드에서 갈 수 있는 모든 길을 다 훑었는지 표시해 이미 검증 끝난 노드를 구분
- _parent: 사이클이 발견됐을 때 "1->2->3->1"처럼 경로를 역추적해서 출력하기 위해 부모를 기록하는 벡터
DeadLockProfiler.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "DeadLockProfiler.h"
/*--------------------
DeadLockProfiler
---------------------*/
void DeadLockProfiler::PushLock(const char* name)
{
LockGuard guard(_lock);
// 아이디를 찾거나 발급 (0부터)
int32 lockId = 0;
auto findIt = _nameToId.find(name);
if (findIt == _nameToId.end())
{
lockId = static_cast<int32>(_nameToId.size());
_nameToId[name] = lockId;
_idToName[lockId] = name;
}
else
{
lockId = findIt->second;
}
// 잡고 있는 락이 있다면
if (_lockStack.empty() == false)
{
const int32 prevId = _lockStack.top();
// 여기서 prevId는 본인 스레드가 걸었던 이전 lock을 가져와야 함
// 본 코드에선 _lockStack을 DeadLockProfiler에서 한꺼번에 관리하기 때문에
// 다른 스레드가 걸었던 lock을 본인이 걸었던 이전 lock이라고 착각하고 이상한 간선을 만들게 됨
// 다른 스레드와의 데드락을 감지하는 장치는 _lockHistory와 CheckCycle()이고
// _lockStack은 각 스레드가 어떤 순서로 lock을 잡고 있는지를 나타내는 것임
// _lockStack은 이 정보(현재 스레드가 잡은 lock 순서)를 활용해 _lockHistory에 간선을 추가하는 역할을 함 (마지막에 잡은 lock에서 현재 잡고자 하는 lock으로 간선을 추가)
// 현재 구현한 RW Lock이 재귀적 락을 허용하는 중임
// 재귀적 락 상황이면 의미가 없기 때문에 그냥 넘어감
// (새로운 간선이 아니라 A -> A 같은 본인 노드로 돌아오는 간선)
if (lockId != prevId){
// 기존에 발견되지 않은 케이스라면 데드락 여부를 다시 확인 (사이클 판별)
set<int32>& history = _lockHistory[prevId];
if (history.find(lockId) == history.end())
{
history.insert(lockId);
CheckCycle();
}
}
}
_lockStack.push(lockId);
}
void DeadLockProfiler::PopLock(const char* name)
{
LockGuard guard(_lock);
if (_lockStack.empty()) // 혹시 모를 스택 비어있을 에러 예방
CRASH("MULTIPLE_UNLOCK");
int32 lockId = _nameToId[name];
if (_lockStack.top() != lockId) // 혹시 모를 스택 push 에러 예방
CRASH("INVALID_UNLOCK");
_lockStack.pop();
}
void DeadLockProfiler::CheckCycle()
{
const int32 lockCount = static_cast<int32>(_nameToId.size());
// 초기화
_discoveredOrder = vector<int32>(lockCount, -1);
_discoveredCount = 0;
_finished = vector<bool>(lockCount, false);
_parent = vector<int32>(lockCount, -1);
for (int32 lockId = 0; lockId < lockCount; lockId++)
Dfs(lockId);
// 연산이 끝났으면 정리
_discoveredOrder.clear();
_finished.clear();
_parent.clear();
}
void DeadLockProfiler::Dfs(int32 here)
{
if (_discoveredOrder[here] != -1) // 이미 방문을 했다
return;
_discoveredOrder[here] = _discoveredCount++;
// 모든 인접한 정점을 순회
auto findIt = _lockHistory.find(here);
if (findIt == _lockHistory.end())
{
_finished[here] = true;
return;
}
set<int32>& nextSet = findIt->second;
for (int32 there : nextSet)
{
// 아직 방문한 적이 없다면 방문한다
if (_discoveredOrder[there] == -1)
{
_parent[there] = here;
Dfs(there);
continue;
}
// here가 there보다 먼저 발견되었다면, there는 here의 후손 (순방향 간선)
if (_discoveredOrder[here] < _discoveredOrder[there])
continue;
// 순방향이 아니고, Dfs(there)가 아직 종료하지 않았다면, there는 here의 선조 (역방향 간선)
if (_finished[there] == false)
{
printf("%s -> %s\n", _idToName[here], _idToName[there]);
int32 now = here;
while (1)
{
printf("%s -> %s\n", _idToName[_parent[now]], _idToName[now]);
now = _parent[now];
if (now == there)
break;
}
CRASH("DEADLOCK_DETECTED");
}
}
_finished[here] = true;
}
CoreGlobal.h
extern class ThreadManager* GThreadManager;
extern class DeadLockProfiler* GDeadLockProfiler;CoreGlobal.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "CoreGlobal.h"
#include "ThreadManager.h"
#include "DeadLockProfiler.h"
ThreadManager* GThreadManager = nullptr;
DeadLockProfiler* GDeadLockProfiler = nullptr;
class CoreGlobal
{
public:
CoreGlobal()
{
GThreadManager = new ThreadManager();
GDeadLockProfiler = new DeadLockProfiler();
}
~CoreGlobal()
{
delete GThreadManager;
delete GDeadLockProfiler;
}
} GCoreGlobal;- CoreGlobal에서 GDeadLockProfiler를 선언 및 생성해 줌
Lock.h
class Lock
{
enum :uint32
{
ACQUIRE_TIMEOUT_TIC = 10'000, // 최대로 기다려줄 틱
MAX_SPIN_COUNT = 5'000, // 스핀 카운트를 최대 몇번 돌 것인지
WRITE_THREAD_MASK = 0XFFFF'0000, // 상위 16비트를 뽑아오기 위한 마스크
READ_COUNT_MASK = 0X0000'FFFF,
EMPTY_FLAG = 0X0000'0000
};
public:
void WriteLock(const char* name);
void WriteUnlock(const char* name);
void ReadLock(const char* name);
void ReadUnlock(const char* name);
private:
Atomic<uint32> _lockFlag=EMPTY_FLAG;
uint16 _writeCount = 0;
};
/*----------------
LockGuards
----------------*/
class ReadLockGuard
{
public:
ReadLockGuard(Lock& lock, const char* name) :_lock(lock), _name(name) { _lock.ReadLock(name); }
~ReadLockGuard() { _lock.ReadUnlock(_name); }
private:
Lock& _lock;
const char* _name;
};
class WriteLockGuard
{
public:
WriteLockGuard(Lock& lock, const char* name) :_lock(lock), _name(name) { _lock.WriteLock(name); }
~WriteLockGuard() { _lock.WriteUnlock(_name); }
private:
Lock& _lock;
const char* _name;
};- 이후 Lock.h/Lock.cpp에서 Lock 클래스의 함수들이 매개변수로 lock과 함께 문자열 포인터를 받을 수 있게끔 추가
- 다음과 같이 어느 클래스끼리 락을 잡다가 충돌이 났는지 확인하기 편하게 하기 위함

AccountManager / PlayerManager (데드락 유도)

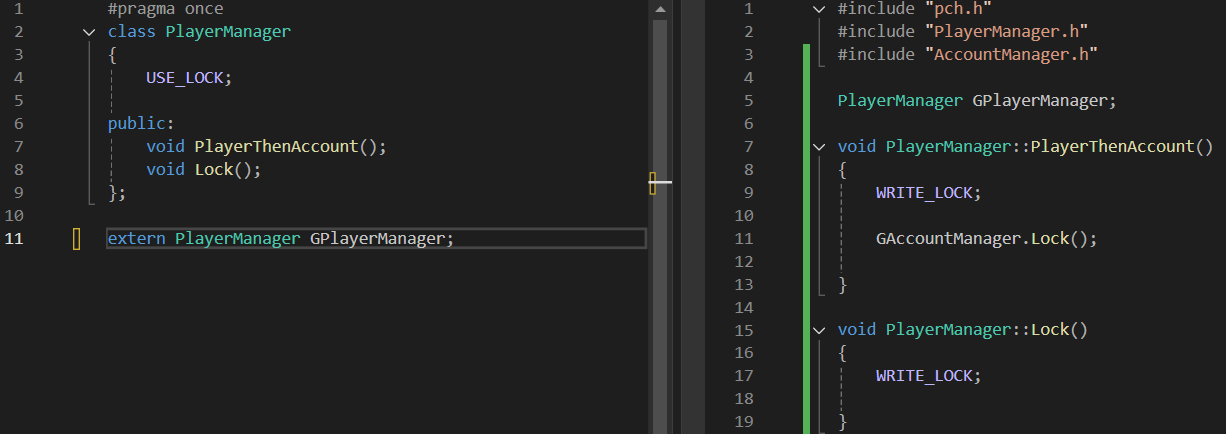
GameServer.cpp (Main)
int main()
{
GThreadManager->Launch([=]
{
while (1)
{
cout << "PlayerThenAccount" << endl;
GPlayerManager.PlayerThenAccount();
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
}
});
GThreadManager->Launch([=]
{
while (1)
{
cout << "AccountThenAccount" << endl;
GAccountManager.AccountThenPlayer();
this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
}
});
GThreadManager->Join();
return 0;
}- 위와 같이 PlayerManager와 AccountManager가 서로 lock을 잡고 풀기 전에 서로를 호출하여 DeadLock을 유발하여 테스트 진행
- 스레드 A(PlayerManager 실행)
- GPlayerManager의 락을 획득 (A 잡음)
- GAccountManager.Lock() 호출 (B를 원함)
- 스레드 B (AccountManager실행)
- GAccountManager의 락을 획득 (B 잡음)
- GPlayerManager.Lock() 호출 (A를 원함)
- (A-1), (B-1) 실행 완료 후, (A-2)나 (B-2)가 실행됐을 경우 데드락 발생
- 스레드 A(PlayerManager 실행)
- Release 모드에선 컴파일러가 최적화를 진행하기도 하고, 다수의 사용자가 한 번에 접하는 라이브 서버 상황을 유도하기 힘들어서 DeadLock 상황이 잡히지 않을 수도 있음
- 컴파일러의 극한의 최적화로 인해 한 스레드가 1, 2를 빠르게 끝내버려서 다른 스레드가 그 사이에 끼어들 수 없는 상황
- 디버그 모드와 라이브 서버일 때의 차이로 인해 발생하는 하이젠버그(Heisenbug) 현상으로 해석할 수 있음
[Troubleshooting] 디버깅이 문제를 해결하는 하이젠버그(Heisenbug)
최종 프로젝트로 서버를 만들어 캠프에서 제공된 클라이언트에 연결하는 과정을 진행하다 ProtoBuf 패킷 통신 중에 에러가 발생했다. 평범한 버그가 아니라 확률 게임처럼 10번 시도에 5~7번 꼴로
dh-0e.tistory.com
- (A-1), (A-2) 사이 혹은 (B-1), (B-2) 사이에 this_thread::sleep_for(1s)을 넣어 그 틈을 만들면 release 모드에서도 높은 확률로 데드락을 유발할 수 있음
이렇게 상황을 직접 찾는 것이 아닌 DFS로 모든 락 경합 상황을 탐색하여 데드락이 발생하는지 확인하기 위해 DeadLockProfiler를 제작하여 테스트한 것
Lock.cpp
void Lock::WriteLock(const char* name)
{
// Profiler에서 lockguard를 사용하고 있는데 lock을 테스트하기 위해서 lock을 사용하는 건 모순적임
// 그래서 디버그 상황에서만 체크를 하도록 매크로 정의
#if _DEBUG
GDeadLockProfiler->PushLock(name);
#endif
// 재귀적으로 동일한 스레드가 이 락을 소유하고 있다면 무조건 성공하게끔
const uint32 lockThreadId = (_lockFlag.load() & WRITE_THREAD_MASK >> 16);
if (lockThreadId == LThreadId)
{
_writeCount++;
return;
}
// 아무도 소유(Write) 및 공유(Read)하고 있지 않을 때, 경합해서 소유권을 얻음
const int64 beingTick = ::GetTickCount64();
const uint32 desired = ((LThreadId << 16) & WRITE_THREAD_MASK);
while (true)
{
for (uint32 spinCount = 0; spinCount < MAX_SPIN_COUNT; spinCount++)
{
uint32 expected = EMPTY_FLAG;
if (_lockFlag.compare_exchange_strong(OUT expected, desired)) {
_writeCount++;
return;
}
}
if (::GetTickCount64() - beingTick >= ACQUIRE_TIMEOUT_TIC)
CRASH("WRITE_LOCK_TIMEOUT");
this_thread::yield();
}
}
void Lock::WriteUnlock(const char* name)
{
#if _DEBUG
GDeadLockProfiler->PopLock(name);
#endif
//ReadLock 다 풀기 전에는 WriteUnlock 불가능
if ((_lockFlag.load() & READ_COUNT_MASK) != 0)
CRASH("INVALID_UNLOCK_ORDER");
const int32 lockCount = --_writeCount;
if (lockCount == 0)
_lockFlag.store(EMPTY_FLAG);
}
void Lock::ReadLock(const char* name)
{
#if _DEBUG
GDeadLockProfiler->PushLock(name);
#endif
// 동일한 스레드가 소유하고 있다면 무조건 성공 (W->R 허용이므로)
const uint32 lockThreadId = (_lockFlag.load() & WRITE_THREAD_MASK >> 16);
if (lockThreadId == LThreadId)
{
_lockFlag.fetch_add(1);
return;
}
// 아무도 소유하고 있지 않을 때 경합해서 공유 카운트(R_L)을 올림
const int64 beingTick = ::GetTickCount64();
while (1)
{
for (uint32 spinCount = 0; spinCount < MAX_SPIN_COUNT; spinCount++)
{
uint32 expected = (_lockFlag.load() & READ_COUNT_MASK);
if (_lockFlag.compare_exchange_strong(OUT expected, expected + 1))
return;
}
if (::GetTickCount64() - beingTick >= ACQUIRE_TIMEOUT_TIC)
CRASH("READ_LOCK_TIMEOUT");
this_thread::yield();
}
}
void Lock::ReadUnlock(const char* name)
{
#if _DEBUG
GDeadLockProfiler->PopLock(name);
#endif
if ((_lockFlag.fetch_sub(1) & READ_COUNT_MASK) == 0)
CRASH("MULTIPLE_UNLOCK");
}- Debug 모드로 진행해서 DeadLockProfiler를 사용하여 데드락을 탐지
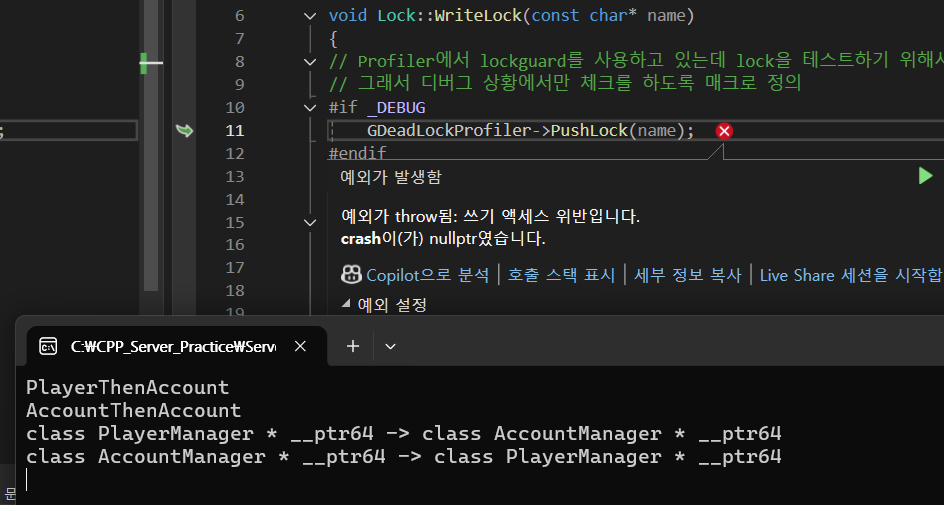
- 다음과 같이 데드락을 찾아서 CRASH를 내는 것을 확인할 수 있음
Release mode vs Debug mode
| 구분 | Debug 모드 | Release 모드 |
| 최적화 | 안 함 (/Od). 코드를 쓴 순서대로 실행. | 강력하게 함 (/O2, /Ot). 실행 속도 최우선. |
| 디버깅 정보 | 상세함. 변수 값 추적, 중단점 가능. | 제한적임. 변수가 사라지거나 코드 순서가 바뀜. |
| 속도 | 상대적으로 느림 (오버헤드 발생). | 매우 빠름. |
| 메모리 체크 | 변수 초기화 체크, 경계 검사 등을 수행. | 그런 거 없음. 잘못 쓰면 바로 뻗거나 쓰레기값. |
| 실행 파일 크기 | 디버깅 정보 포함으로 큼. | 최적화 및 정보 제거로 작음. |
'C++ > Game Server' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++/Game Server] Reader-Writer Lock (0) | 2026.02.12 |
|---|---|
| [C++/Game Server] Thread Manager (+각 서버 file 설명) (0) | 2026.02.11 |
| [C++/Game Server] Lock-Free Stack (with Smart Pointer, Reference Counting) (0) | 2026.02.10 |
| [C++/Game Server] Lock-Based Stack/Queue (+delete, IN/OUT) (0) | 2026.02.05 |
| [C++/Game Server] Thread Local Storage (0) | 2026.02.05 |




